The choice of colour depth and resolution may be restricted by the display capabilities of your computer. If you cannot display 16 million colours in RISCOS, you will not be able to do so in Windows, either.
The PC display contents need to be stored in memory. With the PC Card
this memory actually resides in the Acorn host computer. Here you can specify
a value for how much memory you want to devote to this. This memory is
added to the Wimpslot used by the !PC application. Thus the total RISCOS
memory used by the PC Card is:
- For expansion cards, !PC Wimpslot + VideoRAM
- For second processor cards, !PC Wimpslot + VideoRAM + PCRAM
- Click Select on the Display icon in the PC configuration window.
The following dialogue box will be displayed:
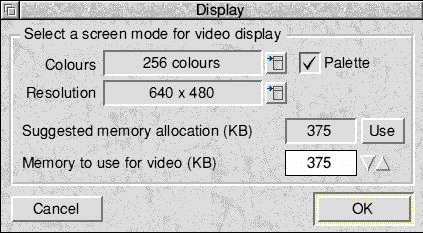
- Click the list button at the right of the Colours option to display a list of colour depths. Pick the one you want by clicking Select on it, bearing in mind the display capabilities of your computer.
- Click the list button at the right of the Resolutions option to display a list of screen resolutions. Pick the one you want.
- Tick the Palette option if you want to use a redefinable palette in 256-colour modes. This is recommended for compatibility.
- When you have made your choices, the configuration software suggests a suitable amount of memory to use. You can increase or decrease this amount by using the arrows in the Memory to use for video (KB) option.
- Note that there is a small speed gain to be had by devoting extra memory
beyond what is actually required, in the range 15 to 60% extra. Only do
this if you have memory to spare: the Suggested memory allocation box
will give a typical maximum figure. Note also that the value given here
is not related to the amount of Video RAM in your machine (see page 44).
- Click OK to confirm your choices and return to the main PC config window.
- Changes in this area are likely – check the Win_readme and Readmefiles for the latest information.